How Are Thermal Paper Rolls Produced?

Modern business operations rely on thermal paper rolls in Point of Sale (POS) systems, ATM receipts and among label printing. They’re invaluable because they can provide crisp, clear images with no ink or toner needed. Have you ever thought about how these indispensable paper rolls are made? In this article we walk you through the fascinating thermal paper roll production process, from raw materials to the finished product.
1. Understanding Thermal Paper
Thermal paper is a specially coated material that will leave an image or text when it is heated. A thermally sensitive chemical coating applied to the surface of the paper is responsible for its functionality. When this coating is exposed to the heat of a thermal printer's print head it undergoes a chemical reaction and produces a visible mark.
Thermal paper has a production process consisting of a number of key steps to ensure durability, clarity and reliability.

2. Raw Materials and Initial Preparation
The trip starts with high quality base paper that is often made of wood pulp. The thermal coating is based on the base paper and must be smooth, strong and have defined thickness.
- Pulp Preparation: A uniform and high grade base paper is produced by refining wood pulp. This is a step in which the pulp is freed from impurities and the pulp has the desired consistency of the fiber.
- Paper Formation: The pulp is prepared, then spread onto a wire mesh to form a continuous sheet. It goes through presses and dryers and is made to the appropriate thickness and moisture content.
This is where the paper is in its standard printing paper form, but the transition to thermal paper will come.
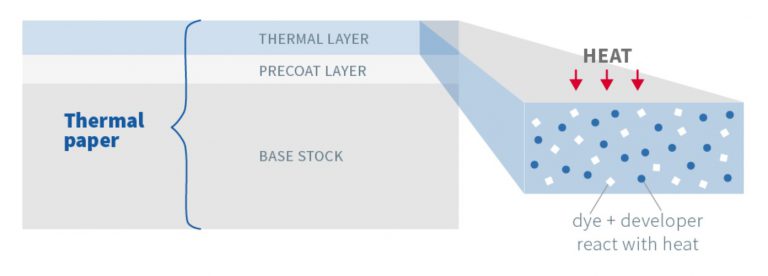
3. Coating Process
The coating process is where the magic of thermal paper begins. Multiple layers of specialized chemicals are applied to the base paper, each serving a unique function.
- Base Coating: This initial layer ensures a smooth surface for the subsequent thermal coating and enhances the paper's durability. It also provides a barrier to protect the base paper from thermal printers' heat.
- Thermal Coating: The critical layer, the thermal coating, contains colorless dyes and developers. These chemicals react under heat to produce an image. A combination of precision rollers and high-tech machinery ensures the coating is applied evenly across the paper's surface.
4. Drying and Quality Assurance
Once the coating process is done, the paper goes through drying to get rid of the excess moisture and to set the chemical layers. The paper is dried with advanced systems, so it won’t warp or curl.
At multiple stages of the process, quality assurance checks are performed. These tests include:
- Thermal Sensitivity Testing: Making sure the paper acts in response to heat.
- Durability Checks: Resistance to smudging, fading and wear.
- Surface Inspection: It can detect defects such as uneven coatings or inconsistencies in thickness. Only paper that meets very high quality standards goes to the next stage.
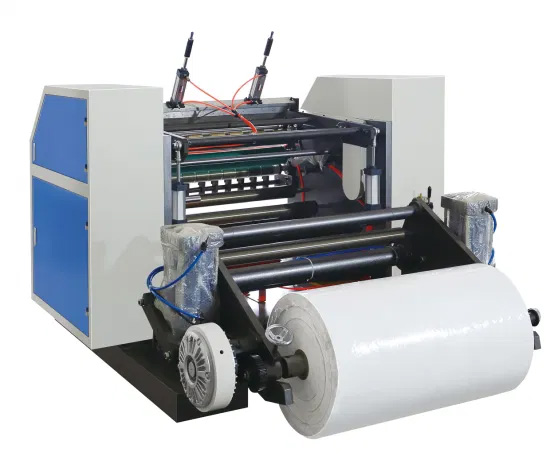
5. To Slit, and Convert into Rolls
After the thermal paper is prepared, they are wound into jumbo rolls. Then these large rolls are cut into the sizes that are appropriate for different applications. The slitting step, during which roll dimensions must be uniform, is a high precision operation.
- Slitting: Jumbo rolls are fed into a slitting machine which cuts them into smaller rolls of different widths and diameters according to customer’s requirements.
- Winding: Tightly wound to be used in thermal printers for smooth feeding, the smaller rolls are smaller.


6. Packaging and Distribution
The thermal paper rolls are then packaged for distribution. The packaging may have branding, protective wrapping, or other labeling to protect and guarantee safe handling and storage, depending on the target market.
- Bundling: Plastic wrapped or boxed together, rolls are protected from dust and moisture.
- Labeling: The specifications of each package include size, length, and compatibility.
7. Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Modern thermal paper production is focused on sustainability. Manufacturers are making eco green practices like sourcing pulp from certified forests and using BPA free coatings. Not only does this help to reduce environmental impact, but it also meets the needs of growing consumer demand for safer and greener products.
Thermal paper production is further made eco friendly through recycling initiatives and the advancement of coating technologies.
Conclusion
Production of thermal paper rolls is a painstaking process which requires advanced chemical formulations, precision machinery and strict quality control. Every step from the raw material selection to the coating to the slitting has been designed to make the paper reliable and performant.
The innovation and expertise behind this everyday product can be seen in understanding how thermal paper rolls are made. With the increasing reliance on thermal paper by businesses, advances in production techniques promise to bring even greater efficiency, sustainability and quality in the years to come.
For more information about thermal paper and its applications, visit Top Roll Paper.

